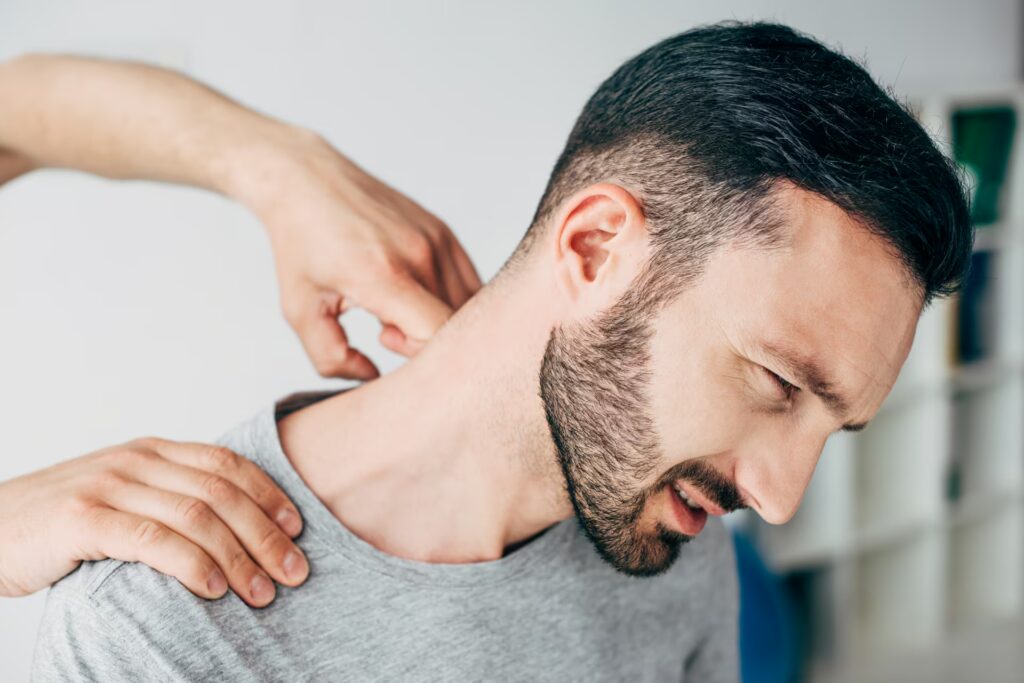

Back & Neck Pain
Back and neck pain are common conditions often caused by muscle strain, poor posture, injury, or degenerative issues like herniated discs or arthritis. Symptoms range from localised discomfort to radiating pain, stiffness, or reduced mobility, impacting daily activities.
Physiotherapy plays a vital role in managing these conditions by addressing root causes and promoting recovery. Through targeted exercises, manual therapy, and posture correction, physiotherapists strengthen supporting muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce inflammation. By tailoring treatment plans to individual needs, physiotherapy helps restore function, prevent recurrence, and enhances quality of life for those with back and neck pain.
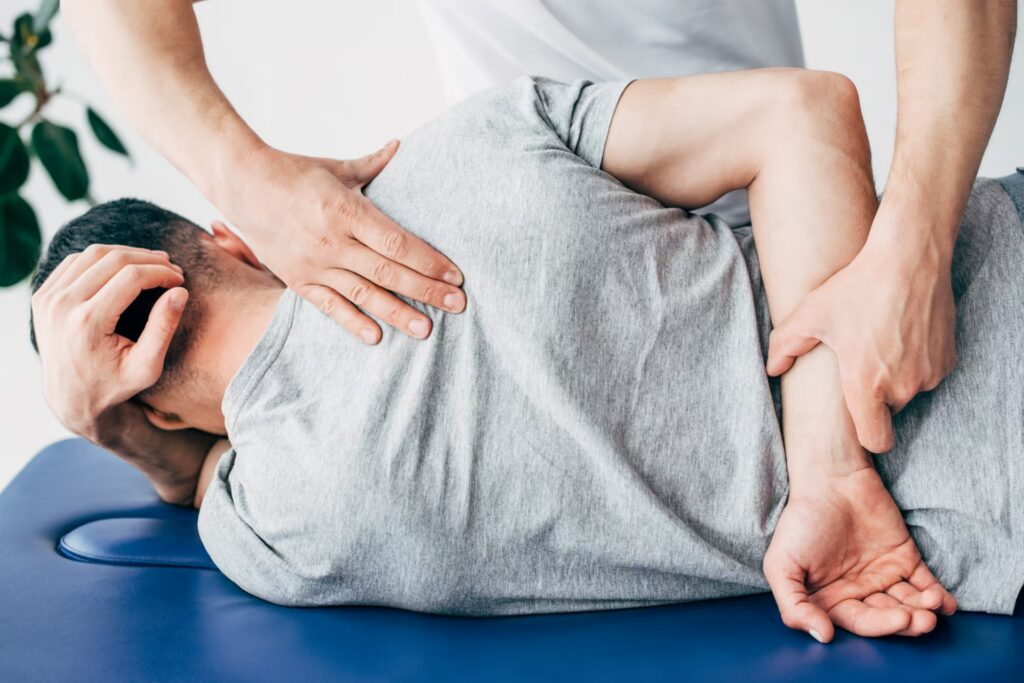

Shoulder Pain
Shoulder pain is a common condition caused by issues like rotator cuff injuries, tendonitis, bursitis, frozen shoulder, or arthritis. It manifests as discomfort, stiffness, or reduced range of motion, often worsened by overhead activities or poor posture.
Physiotherapy is highly effective in managing shoulder pain by addressing its root causes. Through targeted exercises, physiotherapists strengthen shoulder muscles, improve flexibility, and restore joint stability. Manual therapy, such as mobilisation, reduces pain and stiffness. Posture correction and activity modification prevent further strain. By tailoring treatments, physiotherapy promotes healing, enhances function, and prevents recurrence, improving quality of life.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease characterised by cartilage breakdown, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, commonly affecting knees, hips, and hands. It results from aging, wear-and-tear, or injury, leading to inflammation and joint damage.
Physiotherapy is a key treatment for managing osteoarthritis, focusing on pain relief and functional improvement. Therapists design personalised exercise programs to strengthen muscles around affected joints, enhance flexibility, and improve stability. Low-impact activities like swimming are often recommended. Manual therapy reduces stiffness, while modalities like ultrasound or heat therapy alleviate pain. Education on joint protection and weight management further supports long-term management, improving mobility and quality of life.
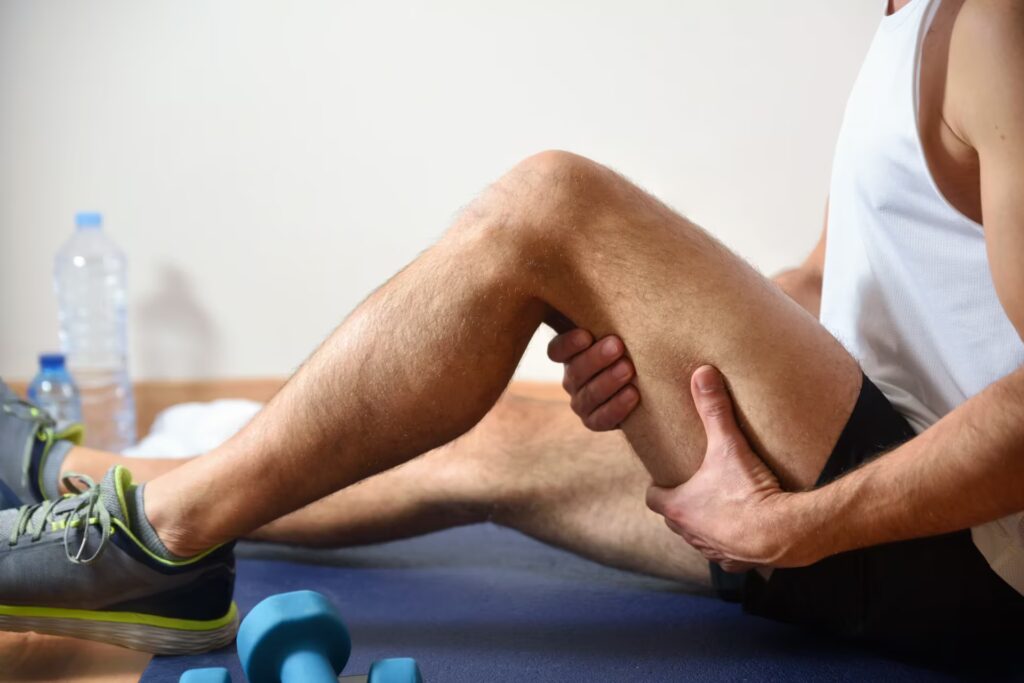

Sports Injuries
Sports injuries encompass conditions like sprains, strains, tendonitis, fractures, or dislocations, often caused by overuse, trauma, or improper technique during physical activity. Common examples include ankle sprains, hamstring strains, or rotator cuff tears, leading to pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
Physiotherapy is crucial for recovery, focusing on restoring function and preventing re-injury. Therapists use targeted exercises to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and enhance coordination. Manual therapy reduces pain and stiffness, while modalities like ultrasound or ice therapy manage inflammation. Education on proper techniques and gradual return-to-sport plans minimises recurrence. Physiotherapy accelerates healing, optimises performance, and supports people in regaining full function.
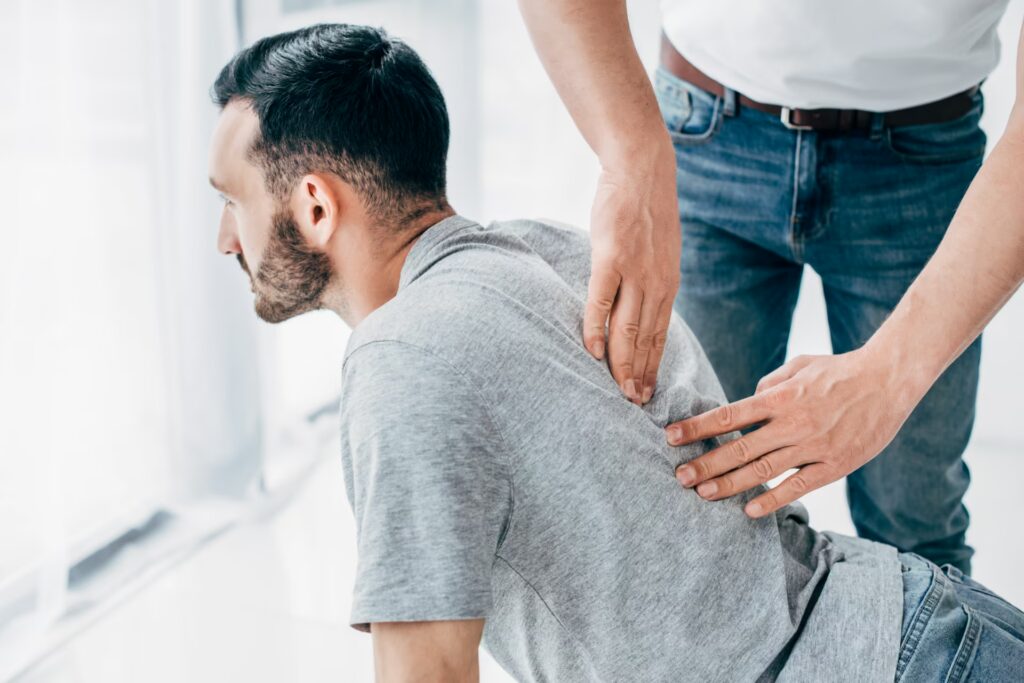

Postural Issues
Posture issues refer to improper body alignment during sitting, standing, or movement, often causing pain, muscle imbalances, and reduced mobility. Common problems include forward head posture, rounded shoulders, or excessive spinal curvature, resulting from prolonged sitting, poor ergonomics, or weak core muscles.
Physiotherapy effectively addresses posture issues by identifying and correcting misalignments. Therapists design tailored exercise programs to strengthen core and back muscles, improving stability and alignment. Manual therapy, such as joint mobilisation, relieves tension and enhances flexibility. Education on ergonomic adjustments and mindful movement habits prevents recurrence. Through these interventions, physiotherapy reduces pain, enhances posture, and promotes long-term musculoskeletal health.
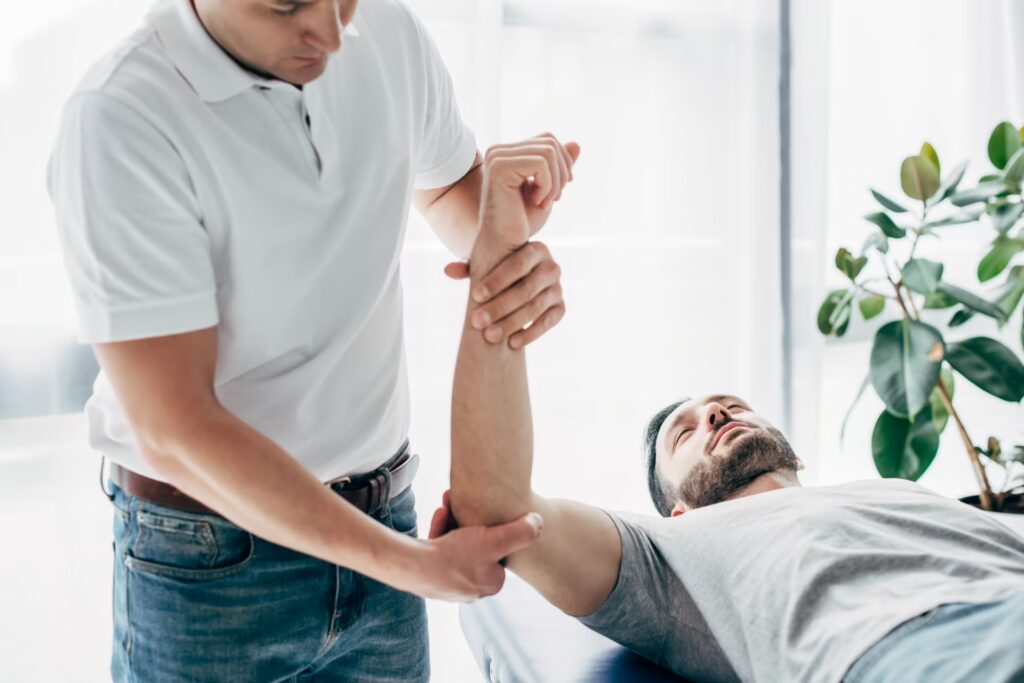

Muscle Strains
Muscle strain, or a “pulled muscle,” occurs when muscle fibres are overstretched or torn due to excessive force, overuse, or improper movement. Common in areas like the hamstrings or lower back, it causes pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
Physiotherapy is highly effective in treating muscle strains by promoting healing and restoring function. Therapists use targeted exercises to gradually strengthen the injured muscle and improve flexibility. Manual therapy, such as massage, reduces tension and pain. Modalities like ice therapy alleviate inflammation. Education on proper warm-up techniques and movement mechanics prevents re-injury. Physiotherapy accelerates recovery, enhances mobility, and supports a safe return to activity.
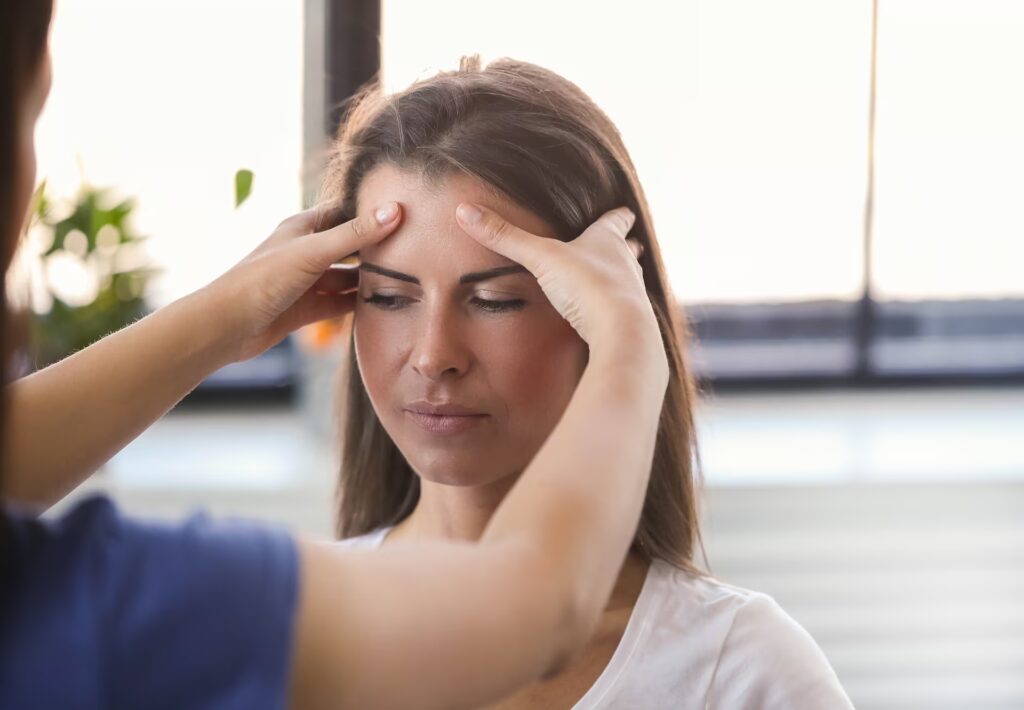

Dizziness & Vertigo
Dizziness and vertigo involve feelings of lightheadedness or a spinning sensation, often disrupting balance. Causes include benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), inner ear disorders, vestibular neuritis, or neck dysfunction. Symptoms range from mild unsteadiness to severe disorientation.
Physiotherapy, particularly vestibular rehabilitation, is highly effective for these conditions. Therapists assess the root cause and use techniques like the Epley maneuver for BPPV to reposition inner ear crystals. Customised exercises improve balance, strengthen neck muscles, and retrain the brain’s vestibular system. Education on movement strategies reduces symptom triggers. Physiotherapy alleviates dizziness, enhances stability, and restores confidence, enabling patients to resume daily activities safely.

1:54
Hip Pain
Hip pain can arise from conditions like osteoarthritis, bursitis, tendonitis, labral tears, muscle strains, or hip impingement, often triggered by overuse, injury, or degenerative changes. Symptoms include discomfort, stiffness, or reduced mobility, impacting daily activities.
Physiotherapy is highly effective in managing hip pain by addressing its root cause. Therapists use tailored exercises to strengthen hip and core muscles, enhancing stability and flexibility. Manual therapy, such as joint mobilisation, alleviates pain and improves range of motion. Education on movement mechanics and activity modification prevents further strain. Physiotherapy promotes pain relief, restores function, and supports long-term hip health.
